Random urine in Boricon container; measured on a post prandial sample taken approximately two hours after a meal stimulus.
Random non-fasting urine in Boricon container.
Stable for 3 days in Boric acid containers at ambient temperature. If unable to send sample immediately, freeze at -20°C and send at ambient temperature in the post. For long-term storage (e.g. to batch samples), we recommend freezing at -80°C.
nmol/mmol/L
Interpretation of Urine C-peptide Creatinine ratio
General points
UCPCR is mainly to be used in patients on insulin treatment to assess endogenous insulin secretion. Its role in patients not on insulin treatment is limited.
If the result of UCPCR is out of keeping with other clinical finding then we would recommend repeating the test especially if it is unexpectedly low. Patients tipping out boric acid preservative from urine collection tube, in a sample taking more than 3 days to reach the laboratory can result in artificially low results (McDonald 2009). We are not aware of any reason for a falsely high value.
Most of the studies have been performed in patients with normal renal function (eGFR >60 mL/min/1.73 m2) but it has been validated in patients with Type 2 diabetes with moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30-60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (Bowman 2011). The test is unlikely to be appropriate in patients with severe renal impairment.
What values are expected in the different subtypes?
The urinary C-peptide creatinine ratio (UCPCR) result is best measured on a post prandial sample taken approximately two hours after a meal stimulus. Thresholds for interpretations of UCPCR in patients with insulin treated diabetes are shown below (TABLE 1)
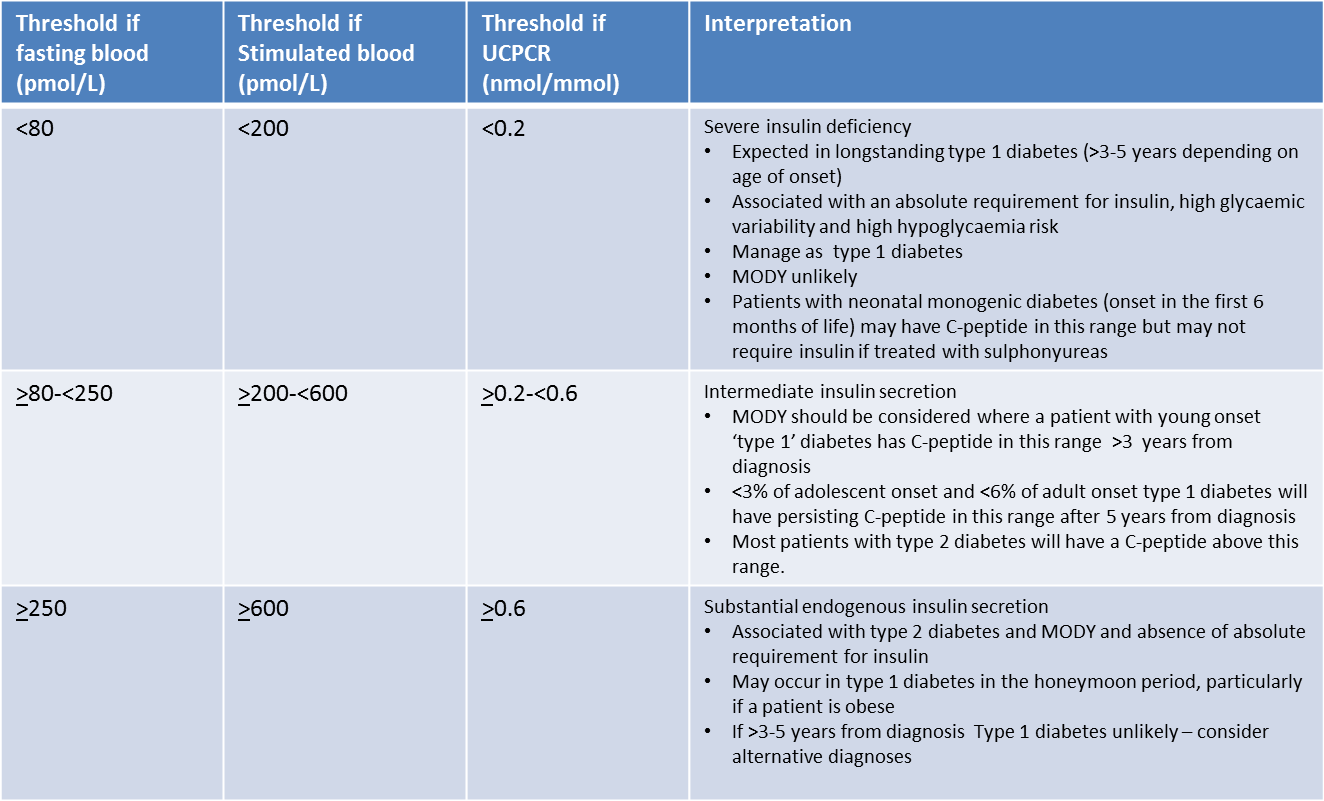
For random non-fasting urine collections, results are strongly correlated with mixed meal C-peptide, with high sensitivity and specificity for identifying clinically relevant thresholds.
If you have any further enquiries please contact Tim McDonald by email: Timothy.McDonald@nhs.net
References
Local test
7 days
Cannot be added on to an existing request
We welcome referrals for UCPCR. If you are a new requestor please complete the following form: New requestor form
We now also have the option to use NPEx for referral requesting.
Further information about sample requirements for this test can be found here: Urine C Peptide – further information
Further information about sample labelling requirements for this test can be found here: Specimen Labelling Procedure
Specimen Labelling Procedure